dot About surge and SPD
Surge in electricity means a sudden increase of current or voltage, and/or a violent oscillation, which is originated mainly from lightning and from switching. Surge has much energy in spite of it's life time very short. When the surge is introduced to circuits of electronic equipment or IT equipment, those equipments are probably malfunctioned, or something go wrong, and or shorten those life time. And sometimes voltage of the lightening strike is so high that could destroy electronic equipments completely. Such a damage of surge increases as high as the electronic equipment is composed more compact and highly integrated of its circuit composition, and nowadays because all of electronic equipments are going to be made of very precise circuit elements, such damages are increasing the more. In general, the surge in electrical line caused from lightning has high voltage so that break down the dielectric material and make flash over certain electrical path, or the surge could be one of reason to induce over₋current in electronic circuits inside equipments, so that circuits come to burn out. There are various paths of the lightning surge flowing into power₋line(or signal₋line). Generally the surge is considered as two cases, direct and indirect lightening surge. Direct lightning surge, the lightning could struck a point of the electrical system directly, would be thoughted not so often because most of building is built with steel frame and lightning₋rods over the building working as electric shield, but once the direct lightening surge introduced in electrical lines, there might be little of equipments could be avoid a damage at all because this is the most destructive case. The indirect surge might be generated in electrical or signal lines when the system(line) is near the direct₋stroke lightning point, even though the lightning₋rod is. Even if the electric system or earth line is well₋isolated from that point and could be considered safe, when huge current with high current passes through certain path(even if it is intentional or incidental) in very short time, magnetic field variation caused by that current induce lots of surge in neighbor circuit which is coupled in magnetically with this current path. This is often called as induced lightning surge and could appear in a level nearly the one that is arose from direct stroke lightning. Another surge could be found in a electrical or communication line between the lightning spike point and the normal point that is not opened to the that lightning. The reason of this kind of surge current is mainly earth potential differences of each earth points. Damages of these two cases are the most case of damages in general, and levels of the damage is different depending on it's environmental conditions. Even if this case is it's environment of earth’s conductivity is bad, and so the lightning current can't be disperse easily around the earth plane, but the current that is flowed into it's earth line could damage equipments that are connected together by earth line. In IEC 61643₋11, the statics of wave₋form of surge is defined for test. 8/20㎲ wave₋form for current and 1.2/50㎲ wave₋form for voltage is used for test. The sign slash(/) is the datum. The front one means the rising time when it rises to peak value, the following one means the decay time, the time from starting point to the point of the level is reduced half of maximum amplitude.
SPD(Surge Protective Device) is a device to protect electric or electronic equipments from electrical surge. It is installed on the electric line or signal line, and is to disperse the surge energy to earth level quickly in several nano₋seconds. Surge current is diverted its path from lines to earth plane and then surge voltage is reduced to certain suppressed level. So the sensitive electric or electronic equipments can be protected from surges. SPD is one portion of LPS(Lightning Protection System). Especially, if there is not well₋designed earthing system, the SPD installed can't be expected to work well. Therefore, build well₋designed earthing system in conformity with IEC has to be preceded before SPD installing. The choice of SPD is important also for protection. SPDs satisfying IEC(International Electro₋technical Commission) Standard is recommended too. IEC61643₋12 and IEC61643₋21 will help you for selecting and appling SPD.
[Roots of lightning surge flow in]
[8/20 waveform of surge current]
[1.2/50 waveform of surge voltage]
[Concept of SPD's function]
dotGlossary of Specifications
- Test class:
Classification of test method according to KSC IEC 61643₋11 Standards. Indicating as ‘Class I’, ‘Class II’, and ‘Class III’.
- Nominal discharge current (In) :
Crest value of the current through the SPD having a current wave shape of 8/20 microsecond. This is used for the classification of SPD for class II test and also for preconditioning of the SPD for class I and class II tests.
- Voltage protection level (Up) :
Parameter that characterizes the performance of the SPD in limiting the voltage across its terminals. This means limit of influence to equipment from the surge energe while SPD work. So the more the value is small, the more good it is(marked 'Up' in IEC). There is so many SPDs in market which is marked just 'Up' value as less than 1000V. But if manufacture do not mark 'Up' with 'In' and 'Safe Mode', it is like cheating consumer.
- Maximum continuous operating voltage (Uc) :
Maximum voltage which may be continuously applied to the SPD’s mode of protection. In general, this is 10 to 40% up to their nominal voltage. If the SPD has some low value of it, it has less life and it could make SPD out of order and that cause dangerous situation.
- Modes of protection :
SPD protective components (terminals) may be connected line to line or line to earth or line to neutral or neutral to earth and combination thereof. These paths are referred to as modes of protection.
- Voltage limiting type SPD :
SPD that is consist of components like MOV, whose resistance is very high when no surge, but reduced continuously with increased surge current and voltage when the surge voltage is up to the specified value.(components like MOV usually have high resistance.) Most of SPDs consist of MOVs requisitely, and it's quality influence SPD's one.
- Voltage switching type SPD :
SPD that has a high impedance when no surge is present, but could have a sudden change in impedance to a low value in response to a voltage surge. It is similar to Voltage Limiting type SPD, but it's capacity of surge current is relatively bigger than that of voltage limiting type. And it's response time and recovery time is somewhat longer than that of previous MOV. Because of this property, it is applicable between conductors of which the potential difference is negligible in ordinary state such as the neutral to earth so as to make equipotential when surge is engaged on those. Neutral₋Earth lines which has no voltage, so that the SPD could protect the system against surge with both of safety and durability of power services.
- SPD Disconnecting Devices :
If the voltage sustained by SPD is abnormally high continuously, an internal component probably damaged to increase temperature suddenly and so the SPD is to be hazardous of fire or explosion. To prevent such hazardous of SPD, there must be used a kind of disconnecting devises like a circuit breaker on a fuse. Modern SPD generally has a fuse that is thermally coupled with MOV inside to prevent this hazardous state and this type of SPD has a probability of safety most of all.
- Leakage Current of SPD :
When SPD had been operating for a long time and experienced many surges, then SPD might be tired and deteriotrated on their performances and there could be found some leakages caused by SPD. Such little leakages may have no problems but in accordance some leakage could make potential differences around earthing system which is danger to personnel and has a probability of fire hazard. It is needed to check the leakage periodically so that, if need, some of SPD is to be replaced by new one.

[MOV and GDT]
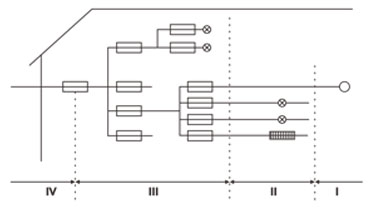
1) 카테고리 I : 옥내콘센트에 접속 기기(정보통신기기)
2) 카테고리 II : 옥내콘센트, 고정된 전기설비에 접속되는 기기(가전기기, 포터블 기기)
3) 카테고리 III : 옥내 고정된 전기설비에 접속되는 기기(케이블, 버스덕트, 접속함, 스위치, 콘센트등의 배선시스템, 공장등에서 영구적으로 접속되는 기기)
4) 카테고리 IV : 전기설비 인입점, 전력량계, 과전류보호장치를 포함한 가공선 등
[Categories by surge intensity]
설비의 공칭전압 |
필요한 임펄스 내전압 |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
3상계통 |
단상계통 |
카테고리IV |
카테고리III |
카테고리II |
카테고리I |
- |
220 |
4 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 0.8 |
220/380 |
- |
6 | 4 | 2.5 | 1.5 |
[카테고리별 기기의 내전압]